Solar panels are a cornerstone of sustainable power solutions, transforming sunlight into usable power. The size of these panels is a crucial factor in their application, efficiency, and installation. This article explores the dimensions of solar panels and delves into the practical aspects of their use.
Understanding Solar Panel Sizes
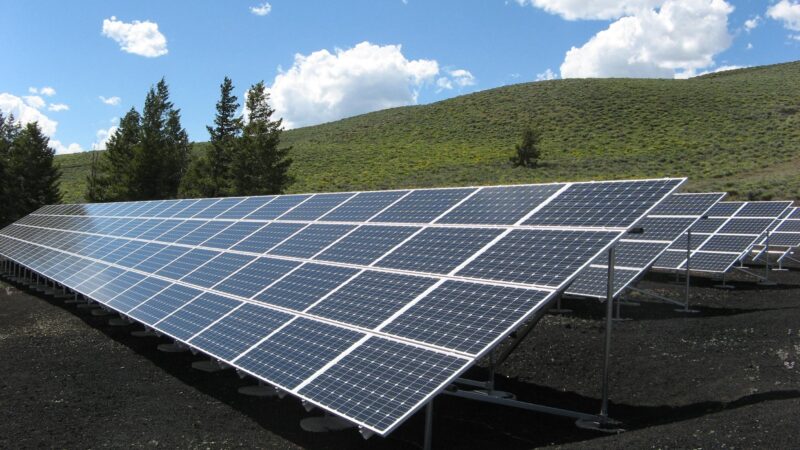

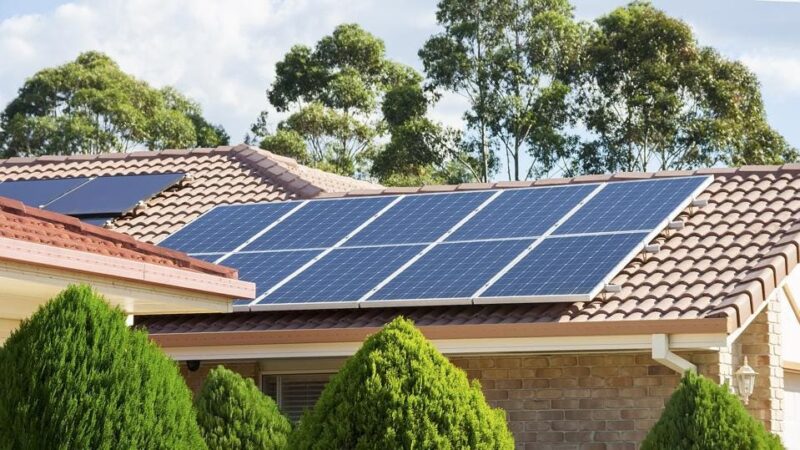
Solar panels come in various sizes, primarily influenced by their intended use and the type of solar cell technology used. Residential solar panels, commonly seen on rooftops, differ significantly in size from those used in large-scale solar farms. Check out this website for additional info and a sizing chart.
Residential Solar Panels
Typically, residential panels measure about 65 inches in length and 39 inches in width, with a depth of around 1.5 to 2 inches. However, these dimensions can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and the model. These panels are designed to fit comfortably on most rooftops, balancing the need for power generation with aesthetic and structural considerations.
Commercial and Utility-Scale Panels
Commercial and utility-scale panels are generally larger, aiming to maximize power output in vast solar farms. These can be up to 78 inches long and 39 inches wide. The increased size allows for more cells to be incorporated, enhancing the panel’s power capacity.
Weight and Portability
The weight of a panel is a key factor, especially for rooftop installations. On average, a standard residential solar panel weighs around 40 pounds. This weight ensures the panel is light enough for easy handling and installation but robust enough to withstand environmental stresses.
For portable solutions, such as those used in camping or emergency power supplies, solar panels are much smaller and lighter. These can weigh as little as 2-3 pounds and fold down to a compact size for easy transport.
Solar Cell Types and Their Impact on Size

The type of cells used in a panel influences its size and efficiency. The two main types of solar cells are monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
Monocrystalline Solar Cells
Monocrystalline cells are made from a single crystal structure, making them more efficient at converting sunlight into power. They are typically smaller in size compared to polycrystalline cells but offer higher efficiency rates.
Polycrystalline Solar Cells
Polycrystalline cells are composed of multiple crystal fragments. They are larger in size and slightly less efficient than monocrystalline cells but are more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for large-scale installations where space is not a limiting factor.
Efficiency vs. Size
There’s a direct relationship between the size of a solar panel and its power output. Larger panels can accommodate more solar cells, which translates to higher power generation. However, efficiency is also a critical factor. A smaller, more efficient panel can sometimes produce the same amount of power as a larger, less efficient one.
Installation Space Considerations
When planning a solar panel installation, the available space is a significant consideration. For rooftops, the size and layout of the roof will dictate the number and size of panels that can be installed. Ground-mounted systems, typically used in commercial and utility applications, offer more flexibility in terms of size and layout.
Adaptability to Different Environments

Solar panels must adapt to various environments, from residential rooftops to harsh, remote locations. This adaptability is not just about size but also about design and material choices. In areas with extreme weather, panels are designed to be more robust, often leading to slight increases in size and weight to ensure durability and longevity. Conversely, in urban settings where space is at a premium, smaller, more efficient panels are favored.
Integration with Architecture
In modern architecture, solar panels are being integrated into the design of buildings and homes. This integration often requires custom-sized panels that blend seamlessly with the building’s aesthetics. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly offering bespoke solutions to meet these unique size requirements.
Cost Implications of Size
The cost of solar panels is directly influenced by their size and the technology used. Larger panels with higher efficiency rates are generally more expensive. However, they offer better long-term value due to their higher power output. For those with limited space, investing in smaller, high-efficiency panels may be more cost-effective despite the higher initial cost per watt.
Price per Watt
Understanding the price per watt is crucial when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of different sized panels. This metric helps balance the panel size with its power output and cost, providing a clear picture of the value offered by each panel type.
Maintenance and Longevity
The size of solar panels also impacts their maintenance and longevity. Larger panels may be more challenging to clean and maintain, especially in rooftop installations. However, their construction is often sturdier, which can translate to a longer lifespan. Smaller panels are easier to handle and replace but may require more frequent maintenance due to their more delicate nature.
Impact of Size on Lifespan

The lifespan of a solar panel is typically around 25-30 years. While size does not directly affect lifespan, larger panels may be less susceptible to damage from environmental factors due to their robust construction, indirectly influencing their longevity.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of solar panels is a crucial consideration. Larger panels cover more area and, therefore, have a greater environmental footprint during manufacturing and installation. However, their higher power output can offset this impact over time. Smaller panels, while having a smaller initial environmental footprint, may require more units to meet the same power needs, potentially negating their environmental advantages.
Sustainable Production Practices
The move towards sustainable production practices in the solar panel industry is influencing panel size and design. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on reducing waste and energy consumption during production, which may lead to innovations in panel size and efficiency.
End Note
In summary, the size of solar panels is a multifaceted aspect that affects their application, efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. As technology progresses, we can expect to see more innovations in solar panel sizes and designs, catering to a broader range of needs and contributing more effectively to global sustainable energy goals.
Related Posts:
- Is Colorado School of Mines Football Good? - In…
- How to Install Commercial Vinyl Tiles: Pro Tips for…
- What Is Architectural Glass? A Comprehensive Guide…
- Choosing Between Glass Splashbacks and Tiles: 10…
- What Is Needed for a Certificate of Sponsorship UK?…
- How To Install Kodi On Nvidia Shield And Nvidia Shield Pro